Why Are People Worldwide Dreaming About This Man?
/Have you ever dreamed about “This Man”? If you did, did he comfort or befriend you in your dreams? Or was he a malevolent entity that attempted to harm you in your nightmares? If you have dreamed of him, then you are one of thousands across that world who believe to have encountered “This Man” in their dreams at one point or several instances of their lives. This phenomenon became a viral Internet legend several years ago, and websites are also available online which are specially dedicated to describe people’s personal experiences of dreaming of “This Man.”
Background on “This Man”
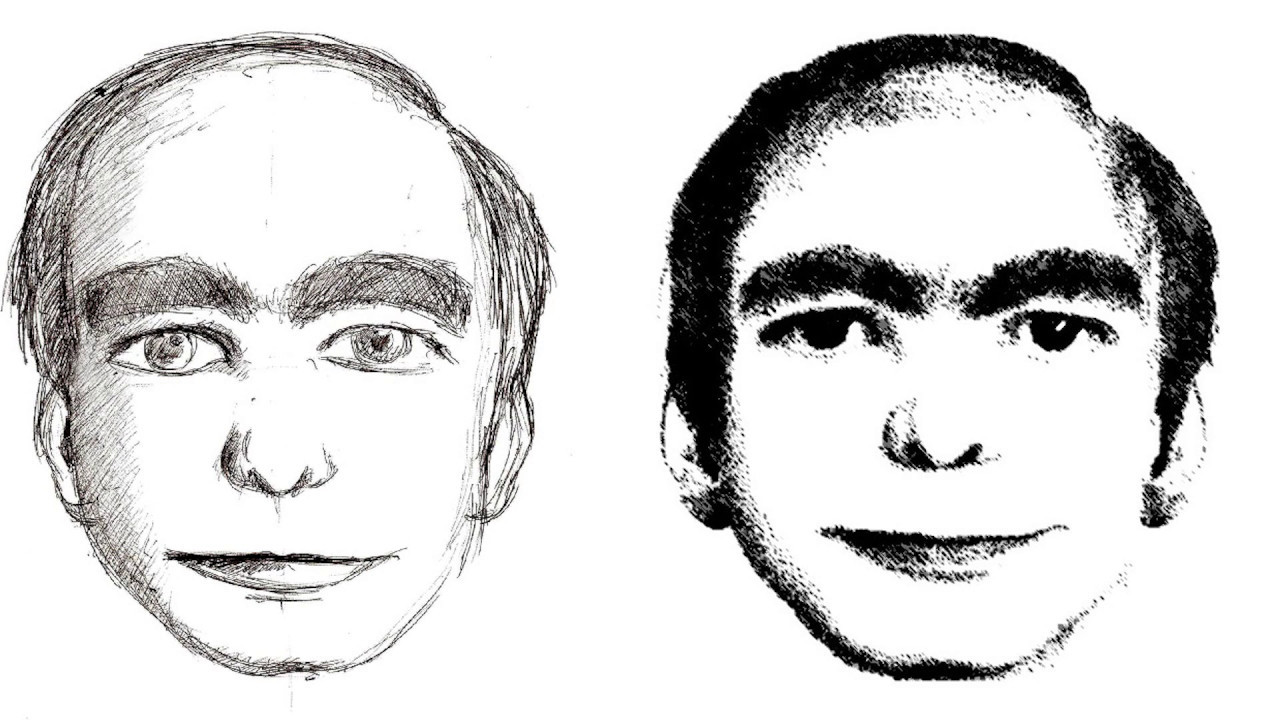
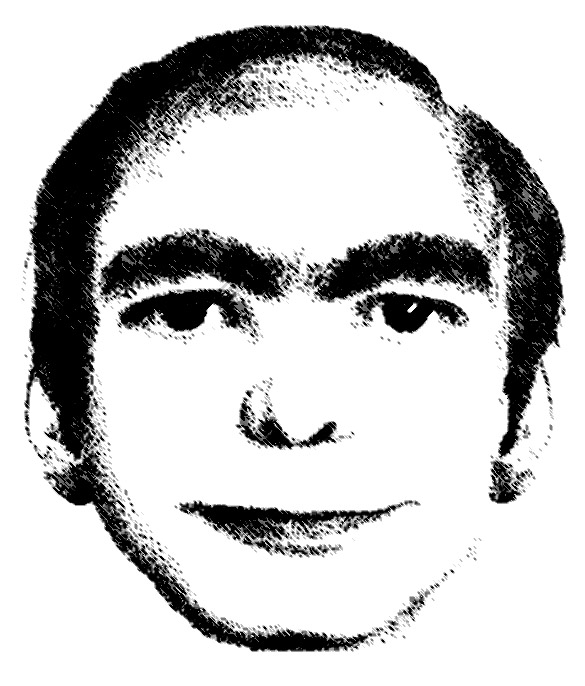
According to the “This Man” website allegedly set up by those who have dreamed about the strange man, every night throughout the world, hundreds of people dream about this man’s face. This dream-related phenomenon supposedly dates back in January 2006 in New York. As the story goes, the patient of a well-known psychiatrist drew the face of a man repeatedly appearing in her dreams. In more than one occasion, the man had provided her some advice concerning her private life, but the woman swears that she never met the man in real life.
The portrait of the man was set aside on the psychiatrist’s desk for a few days until one day another patient pointed out the portrait. He recognized the face in the drawing, saying that the man had often visited him in his dreams. Similar to the claims of the female patient of the psychiatrist, he claims that he has never seen the man in his waking life.
Finding it odd for two people to dream the same stranger, the psychiatrist decided to send the portrait of the man to some of his colleagues who had patients with recurrent dreams. Within just a few months, four patients turned up, claiming to recognize the man as a frequent presence in their own dreams. All the patients referred to the man appearing their dream as “This Man.”
Since the first reported appearance of “This Man” in people’s dreams in 2006, at least 2000 people have reportedly claimed to have all seen the same man in their dreams. The man has allegedly appeared in the dreams of many people in many cities all over the world, including Los Angeles, Berlin, Sao Paulo, Tehran, Beijing, Rome, Barcelona, Stockholm, Paris, New Delhi and Moscow.
According to the “This Man” website, there are currently no ascertained relation or common trait among the people that have dreamed of the strange man. What’s even stranger is that supposedly no real man in the waking world has ever been recognized as resembling the man drawn on the portrait by those who have seen him in their dreams.
Because of this mystery, it has become the ultimate objective of some people to find out the real identity of “This Man” and figure out the reason why he randomly appears in the dreams of a diverse set of human subjects in a variety of unrelated situations.
Theories Allegedly Explaining About “This Man”
The website dedicated to the “This Man” phenomenon has also enumerated and discussed several theories which have supposedly been developed to explain the mysteriously recurring presence of the man in the dreams of a wide variety of people who are not related with each other in any way. Some of these theories are said to have elicited great interest among those who have dreamed of the strange man, and these include the archetype theory, the religious theory, the dream surfer theory, the dream imitation theory and the daytime recognition theory.
Based on Carl Jung’s psychoanalytic theory, “This Man” is speculated to be an archetypal image belonging to humanity’s collective unconscious. This archetype appears in times of a person’s hardship, emotional development, dramatic changes in life and stressful circumstances. And because it is part of the collective unconscious of all people, it makes sense that the man shows up in the dreams of several individuals over the course of several years though they not-at-all related with each other.
There is also another theory about the phenomenon that is founded on religious beliefs. According to this theory, “This Man” is the image of the Creator himself, and that this particular form is one of the many faces in which God manifests himself before mortal beings. And because the appearance of this man is God’s way of revealing himself to people, it is also believed that whatever he utters during the dreams he appears in should be decidedly followed by the dreamers.
The “Dream Surfer” theory is probably the most interesting theory involving the appearance of the same man in the dreams of many people. But while it promises the greatest and most amazing implications, it is also a theory with the lowest scientific credibility. According to this theory, “This Man” is a real person who happens to have the ability to enter the dreams of other people using specific yet unknown psychological skills. There are those who supposedly believe that the man who appears in their dreams looks exactly the same in real life. However, others, on the other hand, think that the man in the dreams looks entirely different from his real-life counterpart. There are also speculations that the man is part of an elaborate mental conditioning plan developed by a powerful corporation.
There is also a scientific psycho-sociological theory which claims that the phenomenon arose casually but has since progressively spread among members of the public by imitation. This means that people who have read or heard about this phenomenon online or through other people who claims to have personally dreamt of the man have become so fascinated and involved with the phenomenon that they started seeing this man in their dreams as well.
Another theory states that apparitions of “This Man” in dreams of people are purely casual. Ordinarily, people do not recall the exact appearance and faces of people they see in their dreams. And so, the image of “This Man” is supposedly an instrument which facilitates the recognition of an undefined image that have appeared during people’s dream states.
“This Man” Is A Hoax
For years, the mysterious story about the same man visiting the dreams of people have spread across various online blogs, discussion forums and even social media communities, where lengthy conversations about the alleged phenomenon’s validity and debunking have ensued.
And so, this leads us to ask a one simple and very important question: Is there really a strange man appearing in the dreams of unrelated people? As it turns out, we never really needed a special theory to explain the “This Man” phenomenon after all, because the whole thing was just one big hoax.
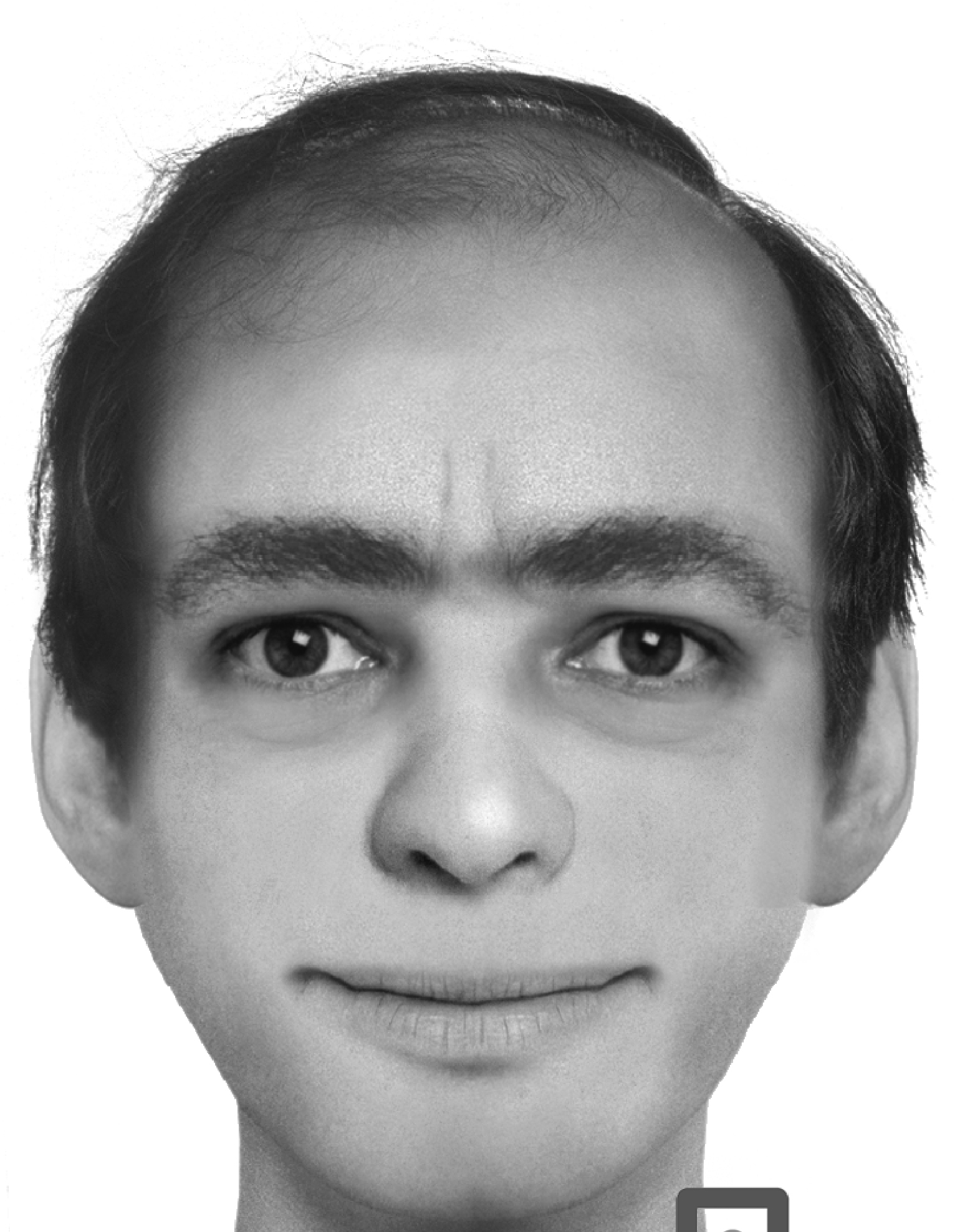
The website – ThisMan.org – is actually the creation of Italian sociologist and marketing strategist Andrea Natella. It was also revealed that Natella runs a company called Guerrilla Marketing, which stages “subversive hoaxes” and creates weird art projects that are mostly about pornography, politics and advertising. The site was also briefly acquired by horror movie production company Ghost House Pictures as part of the promotion for a planned film titled “This Man,” which was supposed to be directed by Bryan Bertino based on a screenplay he also penned.
Regardless of the validity or falsity of this phenomenon, it cannot be ignored that the most-likely real reason “This Man” has gone viral as an internet story is that this fictional entity actually represents the image of “Every Man.” The Face of “This Man” is an amalgamation of many common facial features, which were probably added into the fake portrait showing the man’s face to rouse a sense of familiarity among the public. This myriad of common features may have been the reason why many people from all over the world thought “This Man” looked very familiar as if they had seen him before. And it is this familiarity in this fictional person’s face that has probably perpetuated the viral nature of “This Man.”
Although the “This Man” phenomenon turned out to be just one of many false stories and urban myths that are found online and have gone viral among members of the global internet community, the way that it has piqued the people’s interest and the extent of its impact as a sensationalized, fabricated internet legend cannot be easily dismissed. Neither are the rest of us allowed to be so quick in putting down and ridiculing those who still continue to insist that “This Man” actually exists and that he has actually appeared in people’s dreams. Who knows? Maybe we just don’t have enough evidence to prove that “This Man” is real after all.
Sources:
http://io9.gizmodo.com/5388286/why-are-thousands-of-people-dreaming-about-this-man
http://www.thisman.org/history.htm
http://www.thisman.org/theories.htm
https://www.vice.com/en_us/article/have-you-ever-dreamed-of-this-man-111
http://knowyourmeme.com/memes/this-man-ever-dream-this-man
https://www.vice.com/en_uk/article/we-got-hoaxed-about-that-this-man-dream-haunter-979
http://www.world-of-lucid-dreaming.com/ever-dream-this-man.html
http://www.andreanatella.it/
https://www.facebook.com/thisman.org