Hidden DNA Reveals Extinct Rare Horses Once Wild in North America
/A team of researchers from around the world have been studying the DNA from ancient horse fossils of the mysterious "New World stilt-legged horse." The fossils have been found across North America in the Natural Trap Cave in Wyoming, Gypsum Cave in Nevada, and the Klondike Goldfields of Canada. Dating back to the last Ice Age some 15,000 years ago, scientists have only just begun to crake the code of their ancient DNA lineage.
New "Haringtonhippus Francisci" Horses
Before, researchers thought this stilt-legged horse was related to some modern horses, donkeys, or zebras, but it actually genetically split from modern horses 4-6 million years ago.
"The evolutionary distance between the extinct stilt-legged horses and all living horses took us by surprise, but it presented us with an exciting opportunity to name a new genus of horse," said senior author Beth Shapiro, professor of ecology and evolutionary biology at UC Santa Cruz.
The team decided to name this new horse after a man who spent his career studying ice age fossils in Northern Canada and researched stilt-legged horses since the 1970's. Richard Harington is also emeritus curator of Quaternary Paleontology at the Canadian Museum of Nature in Ottawa.
"I had been curious for many years concerning the identity of two horse metatarsal bones I collected, one from Klondike, Yukon, and the other from Lost Chicken Creek, Alaska. They looked like those of modern Asiatic kiangs, but thanks to the research of my esteemed colleagues they are now known to belong to a new genus," said Harington. "I am delighted to have this new genus named after me. "
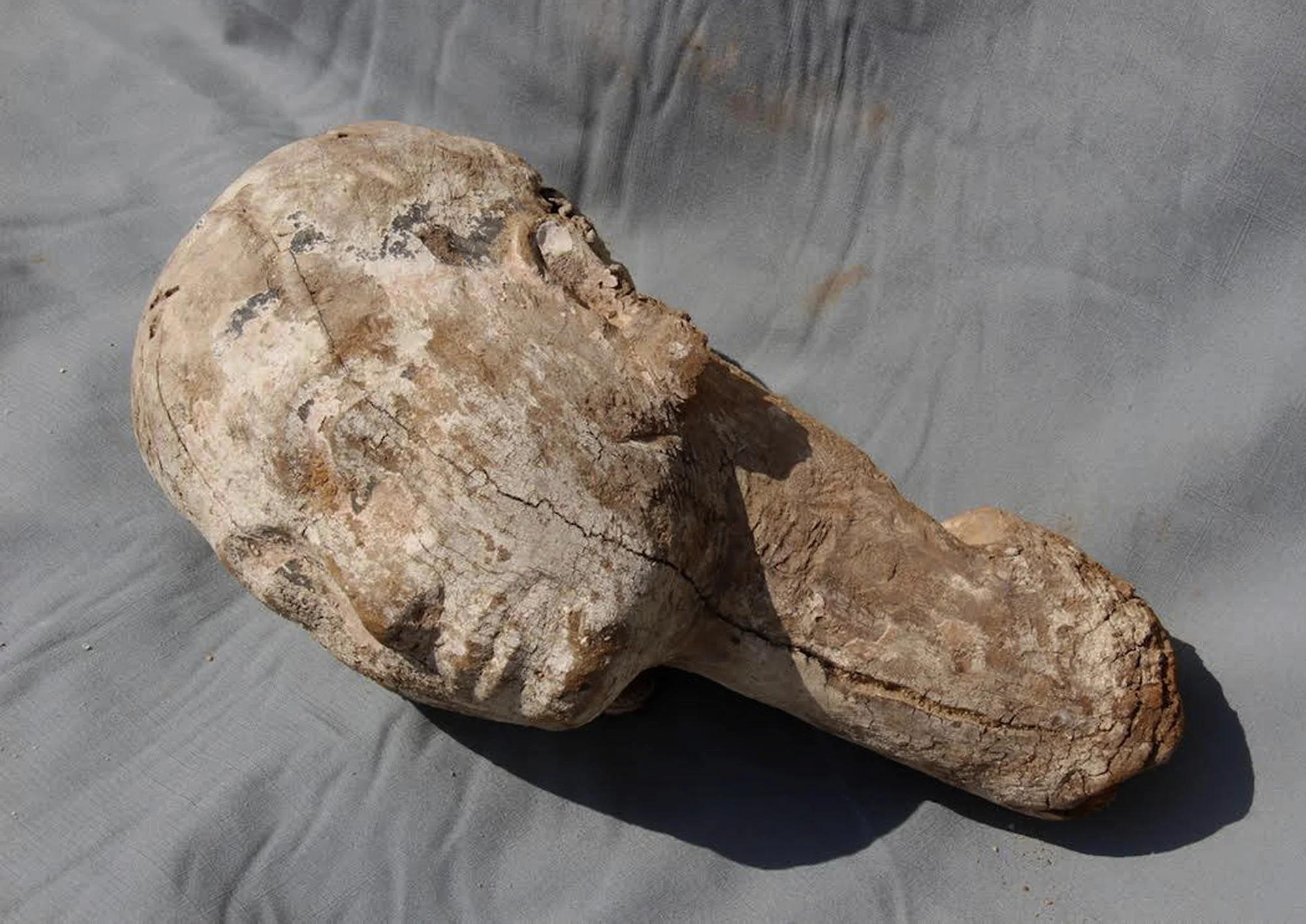
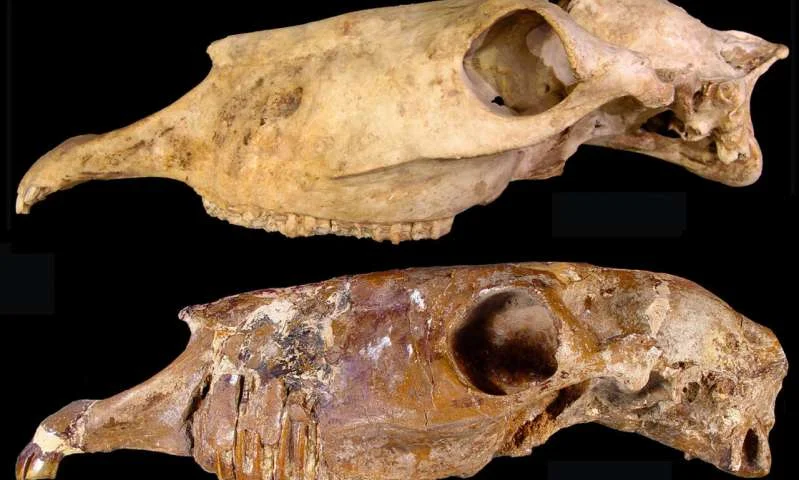
Two skulls of the new genus Haringtonhippus from Nevada (upper) and Texas (lower). Credit: Eric Scott
"The horse family, thanks to its rich and deep fossil record, has been a model system for understanding and teaching evolution. Now ancient DNA has rewritten the evolutionary history of this iconic group," said first author Peter Heintzman, who led the study as a postdoctoral researcher at UC Santa Cruz.
Their studies also reveal the Haringtonhippus francisci did not interbreed with other horse species despite being neighbors. Finding this hidden DNA in younger fossils shows that they also lived 19,000 years longer than previously known. These horses, along with other ancient mammals in North America, were wiped out by the end of the last Ice Age. Fortunately, some horse species in Eurasia survived the freeze, so we can still marvel at their majestic beauty.
"We are very pleased to name this new horse genus after our friend and colleague Dick Harington. There is no other scientist who has had greater impact in the field of ice age paleontology in Canada than Dick," said coauthor Grant Zazula, a Government of Yukon paleontologist. "Our research on fossils such as these horses would not be possible without Dick's life-long dedication to working closely with the Klondike gold miners and local First Nations communities in Canada's North".