The Legendary Sunken Continent of the Kumari Kandam
/We’ve all heard many stories about the Atlantis, the mythical city that the ancient Greeks wrote about in their literature. They were said to be an enlightened and advanced civilization for their time. It was also believed that the whole city met a tragic end, with the ocean consuming it whole and erasing remnants of its people’s culture and legacy from existence.
No one knows for sure whether or not the Atlanteans truly existed as a thriving civilization at some point in our ancient past and if the land they inhabited really had been swallowed by the ocean. And until now, people are still fighting over this issue heatedly, with neither side having any intention of standing down. But did you know that that the tale of the lost city of Atlantis is not the only story involving a sunken land and advanced ancient civilization?
A similar tale has been told in India although it is definitely the less popular one compared to the myth of Atlantis. This lesser-known legend of another lost continent is known as the Kumari Kandam, which is what we will be talking about in this video.
The Legendary Sunken Continent of the Kumari Kandam
The Kumari Kandam is a supposed to be a lost continent located south of modern-day India that occupied a large portion of the Indian Ocean. Also referred to as Kumarikkantam and Kumari Nadu, this massive landmass below the Indian subcontinent is believed to be the home of an ancient Tamil civilization before a catastrophe resulted to its submersion in the deep sea.
The Tamil people are a Dravidian ethnic group whose ancestry can be traced back to Tamil Nadu of India and Sri Lanka. Tens of millions of individuals today identify as Tamilans, making them not only one of the oldest but also largest existing ethno-linguistic cultural groups today. Some of these Tamilans say that the missing Tamil continent of Kumari Kandam is what used to connect the continent of Africa and the landmass of south India. And for the last two centuries, they have declared that this legendary continent is also the hypothesized “lost land” of Lemuria which was developed in the 1890s by Western scholars.
The Hypothesized Submerged Continent of Lumeria
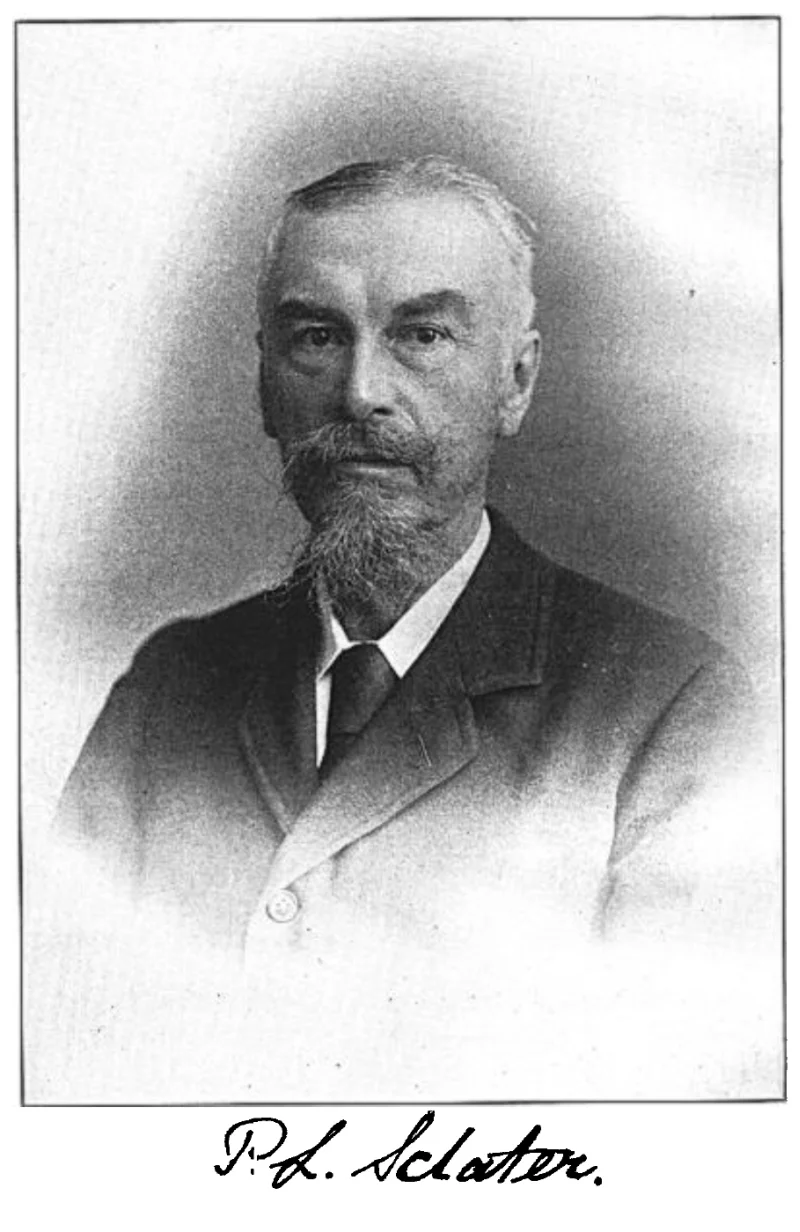
Several scholars in the United States and Europe during the latter part of the 19th century were puzzled by the geological similarities between India, Madagascar, and Africa. English geologist Philip Sclater pondered over the possible reason why there is a significant presence of lemur fossils in Madagascar and India but not in the Middle East or mainland Africa. Sclater went on to publish an article in 1864, titled “The Mammals of Madagascar,” in which he proposed a hypothesis suggesting that Madagascar and India used to be a part of a larger landmass he called “Lemuria.”
Sclater’s Lemuria hypothesis was initially welcomed by members of the scientific community as an acceptable explanation to the way lemurs could have migrated in Madagascar and India in the distant past. However, the theory was eventually discarded after the continental drift theory became the widely-accepted theory in modern times. Nevertheless, the concept of a lost continent below southern India continued to remain popular until the 20th century, especially among the Tamil nationalists who believed Lemuria was the same lost continent they referred to as the Kumari Kandam.
Popularization of Lemuria in Tamil Nadu
According to the Tamil revivalists of the 20th century. Kumari Kandam was the land where the Pandiyan kings once reigned and where the first two Tamil literary academies known as “sangams” were established. And in the 1920s, these Tamil revivalists tried to reduce the domination of the Indo-Aryans and Sanskrit by claiming that prior to the disappearance of Lemuria, it was actually the long-lost Kumari Kandam - the original homeland of the Tamilans and the birthplace of their civilization, language and culture.
The Tamil nationalists did not simply regard the lost land of Kumari Kandam as the home of an ancient Tamil society, but as the cradle of human civilization. They described it as a utopic society where the continent’s enlightened citizens were dedicated to higher learning, trade and commerce, and exploration of the rest of the world. They had established an egalitarian and democratic government that allowed the economy to flourish and its people to thrive.
However, when the continent of Kumari Kandam was lost and the ocean swallowed it whole, the Tamil people had no choice but to migrate to different parts of the world where they established new civilizations.
Submerged Lands in Ancient Indian Literature
Various Tamil and Sanskrit literary works from ancient and medieval times contain legends about a land located south of India that was consumed by the ocean, a catastrophic event believed to have been caused by a tsunami or by a devastating flood. For example, a commentary in the Iraiyanar Akapporul - which is a written work on Tamil poetics from the medieval times - mentions the Pandiyan kings of the early Tamil dynasty and their effort to form three sangams that lasted for thousands of years. The commentary also reveals that two of these sangams were “seized” by the ocean, which ultimately led to the destruction and loss of many ancient writings.
It is important to note, however, that none of these ancient texts or medieval commentaries referred to this lost land that was seized by the sea as “Kumari Kandam.” And none of these literary works have also stated that Kumari Kandam was big enough to qualify as a continent. It turns out that the term “Kumari Kandam” first appeared in the 15-century Tamil version of the Hindu scripture Skanda Purana, and according to cultural historian Sumathi Ramaswamy, the Tamil nationalists used the word “Kumari” - which means “virgin” or maiden” - to symbolize their belief in the purity of the Tamilans’ language and culture prior to their association with the Indo-Aryans.
Criticisms of the Concept of Lemuria
Because the concept of Lemuria is largely recognized by mainstream scholars as a debunked hypothesis today, many experts have frowned upon the alleged attempts of Tamil writers to use the pseudo-scientific theory to validate unverifiable, alternative history. Some historians regard the Kumari Kandam as nothing more than mere fiction founded on mythology and not legitimate scientific research.
Moreover, according to geologists, even if the continental drift theory is set aside and the Lemurian continent did exist at some point in the past, its submersion or dismemberment would have taken place tens to hundreds of millions of years ago during the Mesozoic era. Hence, geological theories like the Lemurian hypothesis should not have anything to do with events in human history that supposedly occurred only a few thousand years ago.
In the end, it cannot be said with absolute certainty that the Kumari Kandam - the land lost to the ocean as described in ancient and medieval Tamil texts - is the same as the hypothesized size and location of the Lumerian continent. At best, we can say that there may be some truth behind such legends. By just how much, there is no way to tell just yet.
For now, this means that while we may be permitted to consider the possibility that the Tamil civilization had once lost a part of its former lands to an ocean-related catastrophe, we cannot claim that this lost land was as big as a continent. If this ancient Tamil landmass did exist in the past, its size can only be compared to that of a small city or a district in today’s standards, making its possible submersion in the sea a few thousand years ago a lot easier to believe.
Sources:
http://www.ancient-origins.net/myths-legends/lost-continent-kumari-kandam-001941?nopaging=1
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Iraiyanar_Akapporul
http://www.crystalinks.com/KumariKandam.html
http://www.ancientpages.com/2016/08/05/kumari-kandam-mythical-lost-virgin-continent-and-history-of-tamil-people-shrouded-in-mystery/
http://www.themysteriousindia.net/kumari-kandam-lost-continent/