Rich Ancient Shipwreck Off Greece Yields More Bronze Statues
/ATHENS, Greece (AP) — Greece's Culture Ministry says archaeologists revisiting one of the most famous shipwrecks of ancient times off southern Greece have found fragments of bronze statues and a section of the wooden hull.
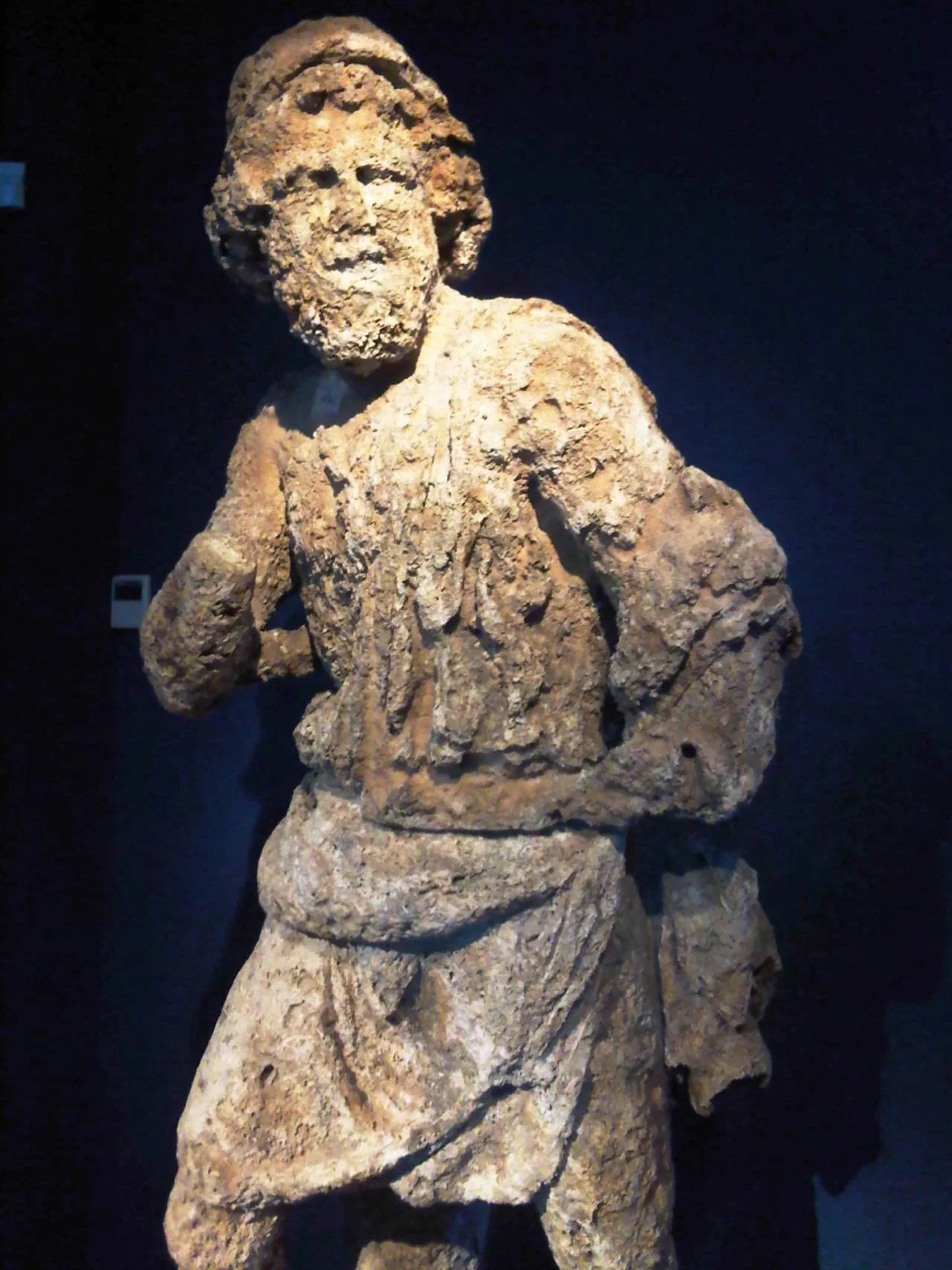
A ministry statement says divers raised a complete arm and a section of pleated clothing from statues, and compacted metal objects that have yet to be cleaned and separated.
Last month's expedition off Antikythera island also located broken bronze and marble statues under large boulders that covered them, probably following an earthquake. Wednesday's statement said these would be investigated during a future excavation.
The 1st-century B.C. wreck of a large freighter discovered more than a century ago has already yielded an ancient astronomical computer — known as the Antikythera Mechanism — as well as statues and thousands of other artifacts.