5 Legendary & Mysterious Armors in History
/History’s most amazing artifacts are the armors ancient warriors wore to battle. Not having the kind of technology we have today, it is amazing to see such intricate and outstanding work that survives to this day despite being battle-worn and suffering many blows in its days.
The skillful hands of a blacksmith are what warriors and knights have to be thankful for. Without them, they would be riding to certain death.
However, our concept and idea of what a battle armor in the ancient days are confined to the clunky, modern-day interpretation of Medieval European armor; those things that you see standing in dark hallways in horror movies or some creepy old guy’s dusty library.
But the ancient world has a multitude of peoples in different countries and each country has a unique culture that is magnified by the clothes they wear, the food they eat, up to the garments they put on during war time.
#5 — The Bronze Helmet (Greece)
The Ancient Greeks are a talented civilization that has given us many things from astronomy to democracy. However, despite our understanding of them being scholars and politicians, the Greeks are also fierce warriors that have one of the most organized armies in the ancient world.
The closest kind of armor that we are familiar with are those that we have seen in movies like Jason and the Argonauts and Clash of the Titans. While there may be similarities between those and their historical inspirations, we are only scratching the surface of what we know about Grecian battle armor.
In 2007, a particular piece of armor was dredged up from Haifa Bay in Israel. It was a Greek helmet made of bronze and ornamented with gold leaves; images of snakes, lions, and a peacock’s palmette also add to the design of the interesting find.
How it ended up in the bottom of the bay is still a mystery to researchers. However, it was not discounted that warriors who travel do lose some of their things such as weaponry, trinkets, and pieces of their garments for whatever reason.
Archaeologists do believe that the helmet belonged to a wealthy Greek mercenary who might have taken part in a series of wars that ravaged the area which dates the helmet as far back as 2600 years old. Also, experts hypothesize that the unknown mercenary who owned the helmet might have fought for an Egyptian Pharaoh named Necho II.
Further research on the helmet also revealed that it had similarities with another helmet found in the 1950s near the island of Giglio, Italy.
“The gilding and figural ornaments make this one of the most ornate pieces of Greek armor discovered,” described Jacob Sharvit, director of the Marine Archaeology Unit of the Israel Antiquities Authority.
#4 — Plant Armor (Oceania and Micronesia)
When we speak of armor, we think about heavy, shiny metal that is double – or triple – the weight of the average warrior. We imagine insanely hot smithies where blacksmiths hammer away at pieces of plate and sheet metal.
However, in the far, coastal regions of Micronesia and Oceania, locals have found an unlikely yet very effective material to make their armor with plants.
While the Greeks are also known to make their protective armors out of plant-based material, it is the warriors from the Kiribati Islands that have perfected the making of it. For the locals of this region of the Pacific, the armor and weapons that they produce were products of readily available material that they could forage such as palm fronds, tree bark, and even animal parts. Combining different materials from land and sea proved to be life-saving implements when battles began to arise.
An example of this kind of armor is constructed using coir, a particularly strong fiber material harvested from coconut trees. Woven together and tightly, it forms an impenetrable layer that protects the body of the person wearing it. Also, like any battle armor, the plant armor comes in several parts that protect almost every part of the warrior’s body – it would even sometimes appear that a Kiribati warrior is more protected than his enemies.
Covered from head to toe, a typical suit of armor from the Pacific and Oceania are a thick woven coat and trousers made of coir, a thicker woven vest, a woven back plate, and a helmet that is usually made out of dried carcasses of porcupine fish.
It is said that the entire suit of armor can withstand projectile weaponry like arrows and spears as well as be able to parry bladed weapons in close quarter combat.
#3 — Skin and Bone (Siberia)
In September 2014, a team of archaeologists from Russia unearthed one of the world’s most mysterious pieces of armor. Made entirely out of bone, archaeologists believe that it belonged to a Siberian knight from 4000 years ago.
What was even more stunning about the discovery was how they discovered it in near-perfect condition.
Buried in the area of Omsk, Siberia, the armor was said to have consisted of several plates of varying sizes to match the wearer’s anatomy all made of bone that was woven together. Suspecting that the bones were from large animals like deer or horse, tests are still being made to find the exact age of the bone armor although, as researchers believe, it is most likely from the Bronze Age.
However, what was quite puzzling about the remarkable find was that it was found to be buried on its own and not alongside a body. Because armor itself had great value during the Bronze Age, it took great lengths to keep it in great condition, and plenty of care and maintenance were required to keep it from deteriorating. The bone armor excavated in Omsk, therefore, suggests that it was buried as a form of offering.
According to Yury Gerasimov, a researcher at the Institute of Archeology and Ethnography in Omsk, the bone armor would most likely have belonged to an elite soldier or warrior. It would have given him “good protection from weapons that were used at the time – bone and stone arrowheads, bronze knives, spears tipped with bronze, and bronze axes.”
Another inconsistency found about the bone armor was that it was far from the style of battle garments worn in that region of Siberia. Experts claim that its design had a much closer resemblance to the cultures of a tribe that originated in the Altai Mountains, a region that is about 1000 km away from where the bone armor was found. This, therefore, led the research team to hypothesize that the bone armor may also be a war trophy or a gift from one culture to another.
#2 — Tatami Gusoku (Japan)
Metal is one of the most common and practical materials used in making suits of armor. Its hardness is highly valued regarding protecting the body of the wearer from attacks.
However, despite skillful design, some suits of armor can still be clunky and difficult to transport when battles are done abroad. However, in ancient Japan, armor was made with the same discipline as they make their legendary swords.
We know the Japanese to be a disciplined race who aim for beauty and perfection in everything they do from pouring tea to clipping branches. The same discipline to perfection is also applied to their one of a kind armor.
Called Tatami Gusoku, it roughly translates as “to fold armor” or “folded armor.” The reason being is that these unique pieces are made in such a way that they can fit into a small box which makes it easy for individual soldiers to transport them.
The armor consists mainly of an armored jacket, a foldable cuirass, as well as a helmet and hood to protect their heads. It had parts that corresponded to a traditional Japanese full suit of armor, the ones we are more familiar with in movies and pop culture.
The Tatami Gusoku is constructed by binding each protective plate with chain mail that links together to form a shirt-like garment. Sensitive parts of the body, such as the chest, had larger plates of metal bound by these chains. Also, the unique construction and material of this suit of armor makes it considerably lighter than its contemporaries and allowed warriors an even wider range of movement since they are not particularly hindered by large and heavy pieces of metal in places where they need to be nimble.
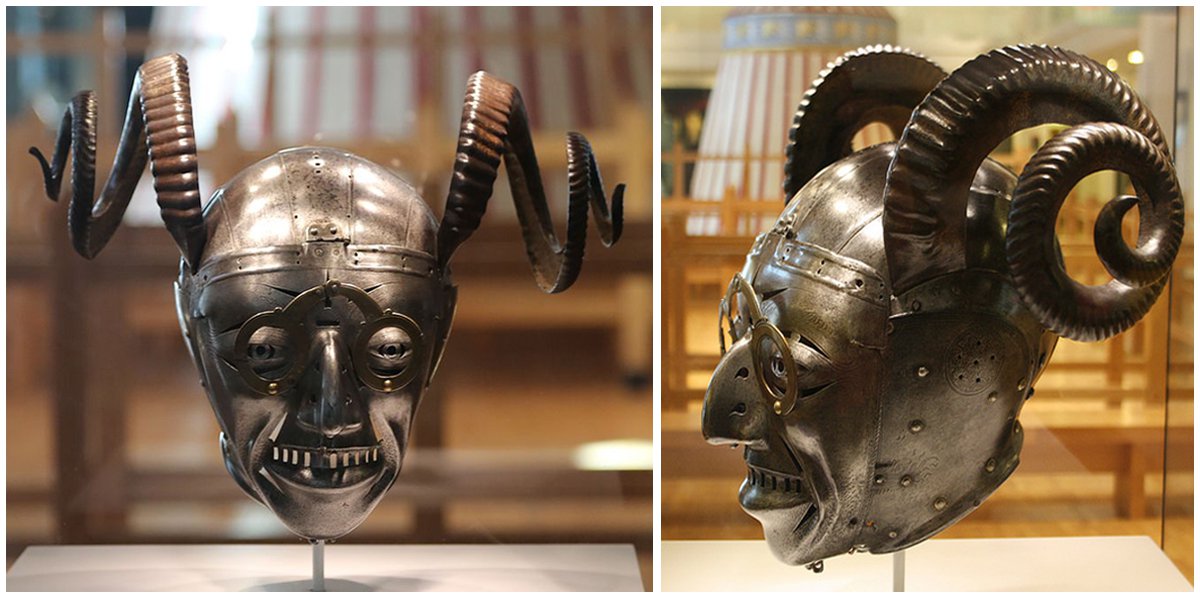
#1 — The Horned Helmet (England)
Designed and made by Austrian goldsmith, Konrad Seusenhofer, the Horned Helmet was originally part of an entire suit of armor gifted by the Holy Roman Emperor Maximilian I to Henry VIII in the 16th Century.
The horned helmet is nothing new in the world of battle armor. Technically, it was not a helmet but an “armet”; a headpiece worn by soldiers that protect his head as well as his entire face during combat. First introduced in the 15th Century, armets were more popular and extensively used in areas of Italy, England, France, and parts of Spain. But for this list, let’s just stick to calling it a helmet.
This particular helmet jumps to the top of our list for its, well… “unique”… looks. Designed to completely cover the wearer’s face, the Horned Helmet resembles the face of a smiling demon with sharp teeth. On its head was a pair of metal horns that twisted outwards. Another peculiar feature of the helmet was a pair of metal glasses that sit on its pointed nose.
Rumor has it that these glasses served a functional purpose because Henry VIII was allegedly near sighted and had a collection of spectacles that was discovered after his death.
It was also rumored that the helmet belonged to Henry’s court jester, Will Somers, when it was first discovered centuries later.
The whereabouts of the rest of the armor are no longer to be found and are assumed to have been destroyed or discarded as scrap metal over the years. Thankfully, due to its grotesque appearance, the helmet was saved from destroyed and is now preserved in the collection of the Royal Armouries in Leeds.
While many suits of armor and helmets were used in battle, this helmet and its now destroyed suit were mainly used by Henry VIII in ceremonies and parades.
Sources:
http://www.ancient-origins.net/artifacts-other-artifacts/more-metal-amazing-historical-suits-armor-007837?nopaging=1
https://www.thevintagenews.com/2016/10/21/japanese-armor-worn-by-all-samurai-classes-the-tatami-gusoku/
http://www.ancient-origins.net/news-history-archaeology/archaeologists-unearth-4000-year-old-siberian-knight-armour-102090
http://www.livescience.com/18700-ancient-helmet-greek-warrior.html
http://warfarehistorian.blogspot.com/2013/03/odd-fighting-units-of-world-history.html
https://www.thevintagenews.com/2017/01/01/henry-viiis-bizarre-looking-horned-helmet-was-designed-for-use-in-parades-rather-than-for-combat/