The Food Chinese Emperors Ate
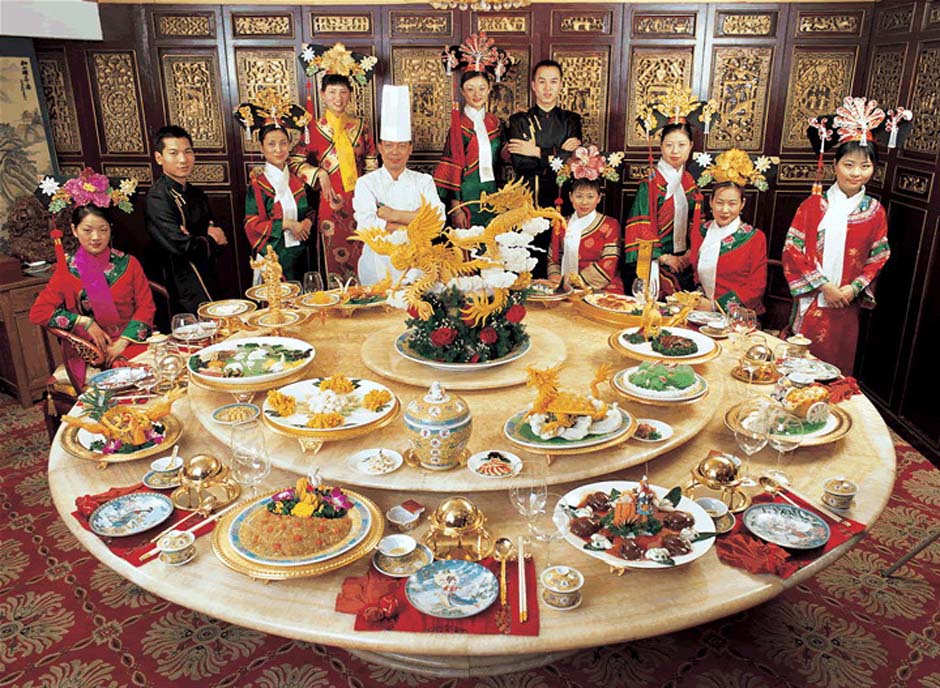
/What kinds of delicious food did the emperors eat in Imperial China? Since the time of emperors living in magnificent palaces, there were such things as imperial foods. Specially prepared meals exclusively for the emperors, their wives, concubines, and royal family members Imperial food represented the best cuisine that a dynasty had to offer. The emperors and those who cater to their health and nutrition used their resources and influence to discover the very best delicacies from across the nation and picked the top cooks to them.
While Imperial food is a reflection of each dynasty's diet, it's also an indispensable part of Chinese cultural heritage that endures even into our modern era.
What is Chinese Imperial Cuisine?
Chinese Imperial Cuisine's diverse cooking styles originated from different Chinese regions and are a collection of various dishes and delicacies that were originally invented by the common people. The royal chefs studied and refined the dishes until fit for an emperor.
The Imperial cuisines are characterized by:
- intricate cooking methods,
- meticulous selection of quality raw materials,
- time-consuming and complicated preparation, and
- elaborate visual presentation.
History of Chinese Imperial Cuisine
Styles and tastes of Imperial Chinese Cuisines differ from one dynasty to another, with each dynasty possessing its own distinctive features. China’s dietetic culture started from the Xia, Shang, and Zhou Dynasties. However, the nation’s imperial cuisine evolved rapidly during the Qin and Han Dynasties' ruling periods and thrived in the Tang, Song, and Yuan Dynasties. It reached considerable heights in the more recent Ming and Qing Dynasties.
Although China’s dietetic culture developed much earlier than the Zhou Dynasty, most agree Chinese imperial food can trace its roots there. Not only was the Zhou Dynasty's Imperial Cuisine an improvement from those prepared in the early Xia and Shang Dynasties, it was also during this period that a complete imperial food management system of the royals and noblemen began. From procurement, diets, and preparation, to staffing, supervision, and the development of meal grades for the members of the imperial family, these responsibilities were handled in accordance with the empire’s established “eating rites.”
As prescribed in the “Rites of the Zhou Dynasty,” “when the emperor took a meal, there were 12 deep bowls with legs and 12 plates. Music was played to urge him to eat.” The rites also indicated that the three daily meals that the emperor would consume included beef, pork, mutton, fish, cured meat, intestine, and stomach.
Even banquets and feasts held by the emperor and his officials had rules to follow. For example, according to the Rites of the Zhou Dynasty, “When the Emperor gives a banquet, there must be six cereals and six animals for food, the six clears for drink, 120 delicacies, eight dainties, and 120 urns of sauce.” The six cereals mentioned in the Rites were rice, broomcorn, wheat, sorghum, millet and wild rice stem, while the six animals the Rites referred to were cow, pig, chicken, sheep, horse, and dog.
Zhou Dynasty
In the Zhou Dynasty, 22 departments were tasked with handling and managing imperial foods prepared and served in the palace. More than 2,300 staff members had different responsibilities and positions in the department like chief cook, internal cook, external cook, assistants, nutritionists, and even wine officers. This complex organization of the royal kitchen assured a detailed and well-defined division of labor that maintained the premium quality of the meals served to the emperor.
Food in Chinese politics became very important during the Zhou, Qin and Han Dynasties, as holding banquets became standard practice whenever the emperor hosted meetings with princes, dukes, or royal family. The imperial food in the later Han and Wei dynasties largely followed this Zhou Dynasty system. However, China’s empowered economy and openness for cultural exchange allowed the palace to attain external sources of raw materials, superior cooking utensils, widespread use of ironware, and higher quality standards for imperial dishes and the skills to make them.
Sui, Tang, & Song Dynasties
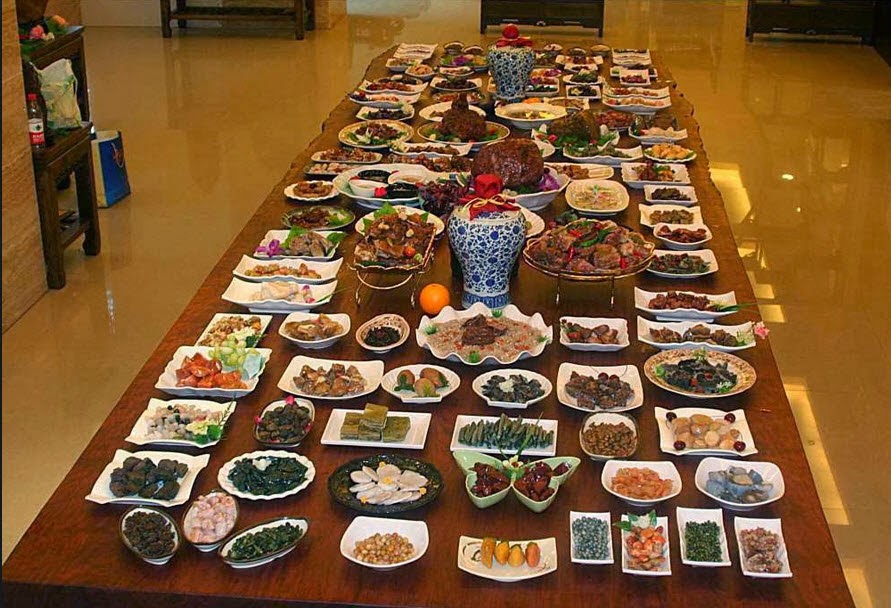
The imperial food of the Sui, Tang, and Song Dynasties also picked up the established system and rules of the previous dynasties, but there were also a lot of changes implemented during these periods in what kinds of food were served to the emperor and members of his family and how they were prepared. There were also more variety in the dishes that were made during these dynasties, as the royal kitchen paid a lot of its attention in diversifying the flavor, tastes, color, and presentation of these dishes. They also took great lengths into naming these dishes. Some popular imperial dishes handed down to us today are quick-friend prawns, fried ringing bells, crab rolls, and steamed Mandarin fish with no soy sauce.
Song & Qing Dynasties
Foods during the Song and Qin dynasties were very similar. However, when the Ming Dynasty usurped Mongolian rule in China, the royal kitchen abandoned the Mongolian food style served to the Yuan emperors. Instead, imperial cuisine during the Ming Dynasty was mostly inspired by Southern Chinese flavors because the emperor preferred it. Protecting the emperor’s health also became an important factor in the preparation of imperial meals, and the rulers of the Ming Dynasty were particularly mindful of protecting their well-being by eating the right healthy foods.
Ming Dynasty
Imperial cuisine of the Ming dynasty was essentially grain-based. At the time, meat and beans were used less in the emperors’ meals compared to their significant use in the earlier dynasties of China. The meat and fish eaten by the emperors were limited to chicken, pheasant, goose, duck, carp, golden carp, Mandarin fish, bream, rabbit, and deer.
The menu in the Ming Palace also changed daily, and the royal kitchen did not repeat the meals and light refreshments they served to the emperors on a daily basis. Some dishes worth noting are shark’s fin soup and edible bird’s nest. Prawns and sea cucumbers were also served in the palace during the Ming Dynasty. Peking Duck, a dish which was first heard of during the Southern and Northern Dynasties, were also fully developed during this time and included in official menus of imperial dishes cooked in the Ming Palace.
There are very few differences between the imperial food served during the Ming Dynasty and the subsequent Qing Dynasty, and even today, the cuisines from these two dynasties remain important to those with Chinese ancestry in different parts of the world. In the Forbidden City, around the imperial rule of the Qing Dynasty, the Imperial Household Department was the division in the Chinese empire’s government that was given the mandate involving the management of the emperor’s meals. There was also a special organization known as the “Imperial Kitchen” in the Qing palace that was tasked with the preparation of imperial cuisine for the emperor.
During the rule of Emperor Qianlong, the kitchens for the imperial tea and meals were separated into two groups: the External Kitchen and the Internal Kitchen. The External Kitchen handled the Qing palace’s official food-related events such as feasts, banquets, and sacrificial rites. The Internal Kitchen, on the other hand, was divided further into departments assigned in the management and preparation of vegetables, meat dishes, roasting, rice cooking, and baking. The meat department, for one, was responsible for cooking delicacies from both land and sea. The bakery was assigned with making cakes and pastries, and the rice-cooking department was the team designated with the preparation of cooked rice and different porridges.
The Imperial cuisine was a significant part of the lives of the royal family members residing in the Qing Palace. The rites of preparing and serving imperial dishes during this time are arguably the greatest of all Chinese dynasties. They included the number of individuals required to make them, and the quality, variety, and cost of the courses served at every meal. Some of the notable dishes of this period were, for example, the Dezhou Braised Chicken – a which is a traditional cuisine that originated from Dezhou in Shangdong Province – and the Wensi Tofu – a soup dish that can be traced back to Jiangsu cuisine.
With how much of its legacy managed to endure until today, Chinese imperial cuisine cannot be dismissed as a minute and irrelevant element of the country’s history. In reality, besides reflecting the dedication, effort, and ingenuity of all the preparers, servers, and inventive common people, Chinese imperial cuisine is also an integral part of all Chinese people's cultural heritage.
Sources:
http://www.cits.net/china-travel-guide/imperial-cuisine-museum-of-china.html
http://www.china.org.cn/english/imperial/25995.htm
http://www.china.org.cn/english/imperial/26109.htm
http://www.china.org.cn/english/imperial/26110.htm
http://www.china.org.cn/english/imperial/26112.htm
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chinese_Imperial_cuisine
http://gbtimes.com/life/forbidden-city-how-did-emperor-eat
https://www.quora.com/What-dishes-best-represent-Chinas-history-and-culture