New Giant Ancient Penguin Discovered in New Zealand
/By MALCOLM RITTER, AP Science Writer
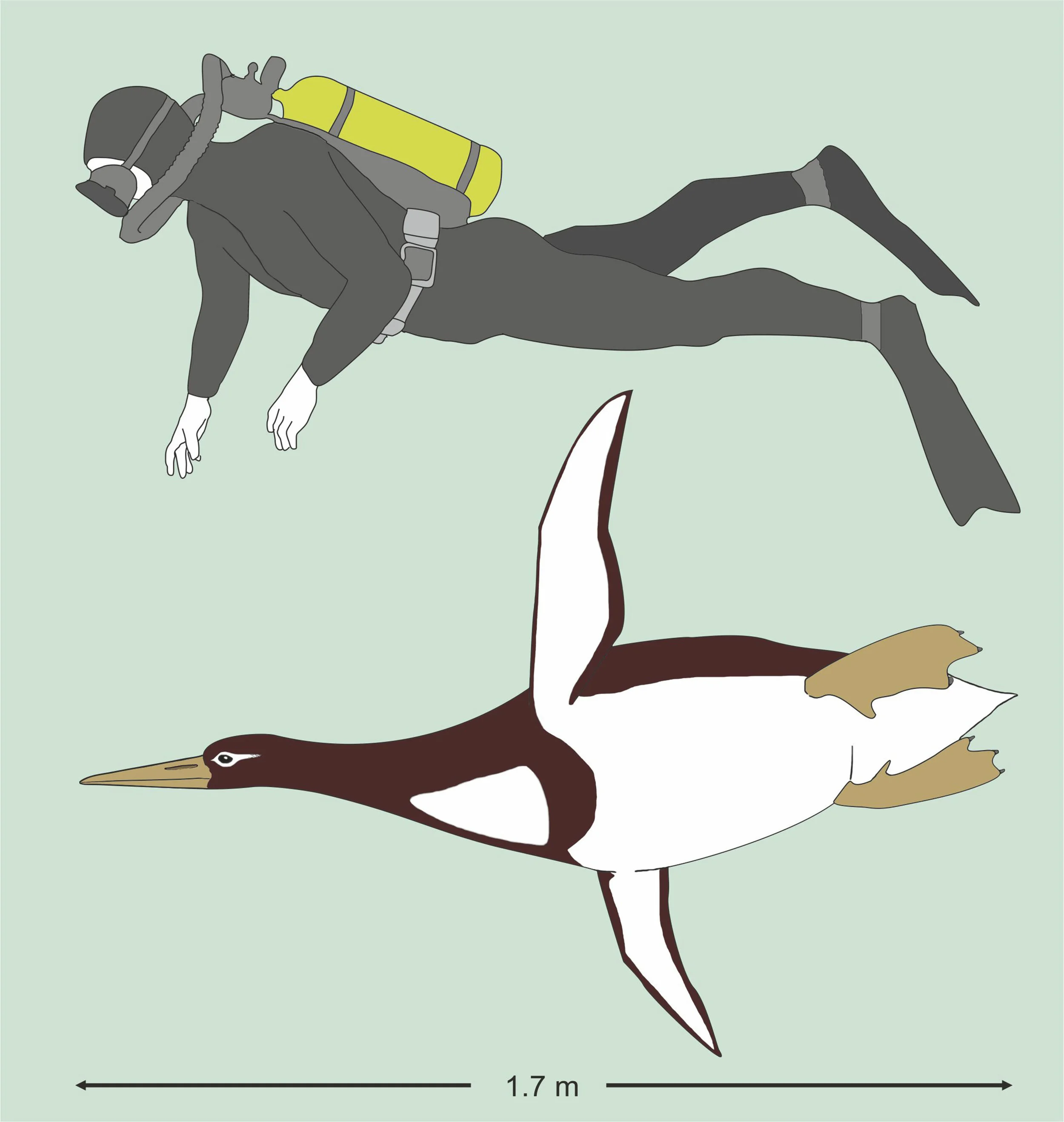
NEW YORK (AP) — Fossils from New Zealand have revealed a giant penguin that was as big as a grown man, roughly the size of the captain of the Pittsburgh Penguins.
The creature was slightly shorter in length and about 20 pounds (9 kilograms) heavier than the official stats for hockey star Sidney Crosby. It measured nearly 5 feet, 10 inches (1.77 meters) long when swimming and weighed in at 223 pounds (101 kilograms).
If the penguin and the Penguin faced off on the ice, however, things would look different. When standing, the ancient bird was maybe only 5-foot-3 (1.6 meters).
The newly found bird is about 7 inches (18 centimeters) longer than any other ancient penguin that has left a substantial portion of a skeleton, said Gerald Mayr of the Senckenberg Research Institute and Natural History Museum in Frankfurt, Germany. A potentially bigger rival is known only from a fragment of leg bone, making a size estimate difficult.
The biggest penguin today, the emperor in Antarctica, stands less than 4 feet (1.2 meters) tall.
Mayr and others describe the giant creature in a paper released Tuesday by the journal Nature Communications. They named it Kumimanu biceae, which refers to Maori words for a large mythological monster and a bird, and the mother of one of the study's authors. The fossils are 56 million to 60 million years old.
That's nearly as old as the very earliest known penguin fossils, which were much smaller, said Daniel Ksepka, curator at the Bruce Museum of Greenwich, Connecticut. He has studied New Zealand fossil penguins but didn't participate in the new study.
The new discovery shows penguins "got big very rapidly" after the mass extinction of 66 million years ago that's best known for killing off the dinosaurs, he wrote in an email.
That event played a big role in penguin history. Beforehand, a non-flying seabird would be threatened by big marine reptile predators, which also would compete with the birds for food. But once the extinction wiped out those reptiles, the ability to fly was not so crucial, opening the door for penguins to appear.
Birds often evolve toward larger sizes after they lose the ability to fly, Mayr said. In fact, the new paper concludes that big size appeared more than once within the penguin family tree.
What happened to the giants?
Mayr said researchers believe they died out when large marine mammals like toothed whales and seals showed up and provided competition for safe breeding places and food. The newcomers may also have hunted the big penguins, he said.